UTICAJ VEŠTAČKE INTELIGENCIJE NA SAVREMENO POSLOVANJE: SCOPING PREGLED
Apstrakt
Svojim ubrzanim razvojem, veštačka inteligencija (VI) postala je značajan faktor koji utiče na savremeno poslovanje, sa važnim implikacijama u različitim organizacionim domenima. Mapiranjem literature o uticaju VI na moderno poslovanje, ovaj rad nastoji da identifikuje relevantne studije i klasifikuje ih prema ključnim oblastima primene, uključujući poslovnu efikasnost i inovacije, korisničko iskustvo, analizu podataka i donošenje odluka, kao i pitanja vezana za etiku, bezbednost i rizike primene VI. Studija se zasniva na sistematskom pristupu pregledu postojeće literature, uz primenu etabliranih metodologija scoping pregleda radi identifikacije i odabira relevantnih studija i istraživanja. Istaknuta su određena ograničenja i praznine u postojećem korpusu istraživanja, koja mogu poslužiti kao osnova i polazna tačka za dalja istraživanja. Na kraju, rad iznosi niz zaključaka i predlaže moguće pravce budućih istraživanja.
Članak
Introduction
The development of information and communication technologies has influenced all aspects of contemporary society (Stanković, Čerović, & Panić, 2023). Very often, companies that were pioneers in adopting innovative technologies over the past twenty years have experienced significant growth and business development. AI is one of the latest advances in this field and a key factor in modern business transformation. According to a PwC report, by 2030 AI could add up to 15.7 trillion US dollars to the global economy (PwC, 2020). However, some authors point out that for a broader application of AI, certain prerequisites must be fulfilled: Natural Language Processing (NLP) for communication in natural language; identification and storage of new knowledge; Automated Reasoning for creating answers and drawing conclusions based on stored information; and Machine Learning (ML) for adapting to new circumstances, as well as for discovering and extrapolating patterns (Russell & Norvig, 2016; Huang & Rust, 2018).
With increasing availability and technological progress (Dašić, Pavlović, & Savić, 2024; Praća et al., 2024), AI has opened numerous opportunities for automation, data analysis, and business decision-making. As a result, companies are facing a growing impact of AI on their daily operations, strategies, and competitiveness. The application of AI in business will lead to fundamental changes in the development and design of user experience (UX), as well as significant improvements in business efficiency using advanced technologies (Butenko, 2018; Ilić et al., 2022).
The main aim of this review is to map the existing literature and to analyze the impact of AI on contemporary business. In addition, the article seeks to identify the key areas where AI has the strongest impact, as well as the benefits and challenges related to its implementation. This literature review provides a broad insight into the current state of research on the application of AI in business environments and examines the implications that arise from this technology. Through the analysis of relevant studies, the article explores how AI transforms business models, improves efficiency of operations, optimizes decision-making, and creates new opportunities for innovation and growth.
This review also considers ethical, legal, and social aspects of AI in contemporary business. Issues such as data privacy, data security, algorithm transparency, and the impact on the workforce are becoming increasingly important in the context of the widespread use of AI.
The analyzed literature emphasizes that AI contributes to contemporary business by increasing efficiency, supporting better decision-making and services, and creating competitive advantage (Dash, McMurtrey, Rebman, & Kar, 2019; Mihajlović & Todorov, 2024). At the same time, it also faces challenges in relation to legal, social, ethical, economic, and regulatory aspects (Di Vaio, Palladino, Hassan, & Escobar, 2020; Krunić et al., 2023).
Through this research, the author aims to clarify the key factors that contribute to the successful application of AI in business environments, as well as to identify the challenges that must be addressed to fully realize the potential of this technology.
Methodological Framework and Data Sources
The methodology applied in this article is based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – Scoping Review extension (PRISMA- ScR) (Tricco et al., 2018; Čavlin et al., 2023; Vladisavljević et al., 2023).
The literature for this review was collected by searching the following databases: Scopus, Web of Science (WOS), EBSCO, and ScienceDirect, as well as platforms such as Google Scholar and ResearchGate. These data sources were chosen because they represent a set of the most relevant scientific results in the fields of business and management. They also enable the organization and integration of academic literature from various sources (e.g., journal articles, book chapters, etc.), which is fully consistent with the methodology used for preparing this review. Figure 1 shows the protocol followed in the selection of relevant studies and sources.
The search keywords included combinations of terms such as “artificial intelligence”, “economic”, “business”, “business management”, “corporation”, “business value”, and “business innovation”. The time frame for the search was limited to publications from 2015 until the end of June 2025, considering the dynamics of digital technology development and the rapid progress of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools.
To ensure the relevance of the selected studies, authors established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Studies included in the review had to deal with the analysis of the impact of AI on different aspects of contemporary business and provide relevant insights into the real-world application of AI in business environments. Excluded were studies that were not available in full text, those outside the scope of this review, articles published before 2015, and studies not available in English, Serbian, or languages related to Serbian.
Following the initial phase of the search, the analysis focused on publication year, abstracts, applied research methodology, key findings, and conclusions. The selected studies were carefully reviewed, and relevant data were extracted to present the impact of AI on contemporary business. The extracted data covered the domains of AI applications, the types of algorithms and technologies used in business processes, and the effects achieved on business performance.
Based on the data collected from different studies, a synthesis of results was conducted to identify key trends and areas where AI has the most significant influence on modern business. Through this analysis, the study examined how AI transforms business models, optimizes processes and decision-making, and creates new opportunities for innovation and growth (Machucho & Ortiz, 2025; Bučalina Matić, et al., 2024; Majstorović & Obrić 2023). Bickley et al. (2022) emphasize that the application of AI in economics has often been discussed in the context of economic history and methodological considerations of various economic fields, while relatively little research has been conducted in finance, macroeconomics, and the creation of monetary and fiscal policies.
This review relies exclusively on publicly available sources. During the preparation of the scoping review, only electronically accessible publications from academic databases such as Scopus, Web of Science, EBSCO, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, and ResearchGate were used. The last search was performed on June 23, 2025.
During the search for relevant literature in the domain of AI impact on contemporary business and the transformation of business models (Figura, Juracka, & Imppola, 2025), various journals in economics, finance, marketing, and digital technologies were used, such as Journal of Business Research, Journal of Strategic Innovation and Sustainability, Journal of Service Research, Journal of Data and Network Science, Journal of Risk and Financial Management, Scholedge International Journal of Business Policy & Governance, Scientometrics, Information, International Journal on Semantic Web and Information Systems, Artificial Intelligence and Social Computing, Information Systems Frontiers, published until June 23, 2025. In addition to these journals, the authors also reviewed conference proceedings from various international conferences published by that date.
In the first iteration of database searches, broad key terms were used. Since the concept of “artificial intelligence” is very general and covers a much wider spectrum than the focus of this study, it was necessary to narrow down the scope by combining specific keywords (Mihajlović et al., 2025). Therefore, the databases and platforms were searched using the following terms and their combinations:
- “AI in economics”, “AI in business”, “AI in marketing”
- “AI and business transformation”, “business value”, “AI and organizational performance”
- “machine learning”, “large language model”, “natural language processing”
- “application”, “impact”, “benefits”, “influence”
Additional literature was identified using the snowball sampling method by reviewing the references of already included studies. No geographical limitations were applied in the search, although it was noted that much of the literature on AI in business originates from East Asia (Ao, 2025). Despite the global scope, the majority of selected publications were written in English. The search was limited to studies and articles published between 2015 and 2025, with results showing that the majority of relevant research has been published in the past four years, coinciding with the broader adoption of AI in society (Jorzik, Klein, Kanbach, & Kraus, 2024).
Selection Strategy and Source Validation
Using the PRISMA-SCR framework, five levels of selection were applied to the identified studies and articles on the given topic. At the first level, the selection focused on the title of the article. Once this criterion was met, the process continued to the second level, which involved the review of keywords.
Figure 1. PRISMA-SCR FLOW Diagram for literature selection
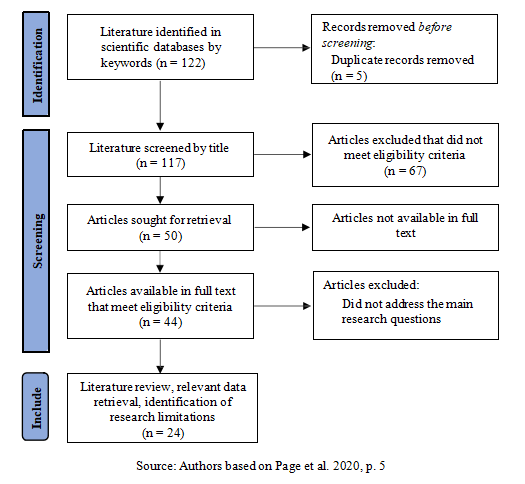
At the third level, the author evaluated the abstracts of the articles that had satisfied the previous criteria. If the article met the requirements at this stage, a full-text review was conducted at the fourth level. Finally, at the fifth level, the conclusions and limitations of the reviewed studies were analyzed.
This review included a total of 24 articles that satisfied all requirements after applying the above criteria. The authors independently developed a matrix for mapping the selected studies. This matrix included the following key data points: names of authors, year of publication, type of article, research area, and key conclusions. Organizing the studies in this way facilitated comparison and the synthesis of results. The articles that remained after the selection of the available literature were thoroughly analyzed and included in the developed matrix for the purpose of synthesizing the results.
We considered a broad spectrum of academic sources important in gathering the literature for this study on the impact of AI on contemporary business (Savić et al., 2025a). The reviewed literature on the impact of AI on contemporary business is considered relevant and provides valid research supported by credible data.
However, it's crucial to stress that we observed several potential limitations. Since AI is still a relatively new phenomenon in the business environment, the lack of empirical data may affect the completeness of the analysis of its impact (Perifanis & Kitsios, 2023). In addition, the rapid technological progress in the field of AI may lead to the quick obsolescence of data and information in certain studies (Savić et al., 2025b).
Given that AI is part of a complex economic and financial system, its influence may be affected by different factors such as geopolitical events, regulatory changes, technological development, and market demands (Bharadiya, 2023; Janković & Golubović, 2025). These factors are difficult to predict and may significantly shape research outcomes.
Despite these limitations, it is important to stress that the existing literature still provides valuable insights. To gain a more comprehensive understanding of this topic, future research should aim to address these limitations and include broader perspectives to create a more complete picture of the impact of AI on contemporary business (Kitsios & Kamariotou, 2021; Sira, 2022).
Integration of Key Findings
The synthesis of this research followed several key steps in the preparation of the study. This included a comprehensive review of all collected sources and the recording of key findings, research methods, and identified limitations. Notes were then grouped according to relevant themes and subthemes related to the impact of AI on contemporary business. The main topics emerging from the reviewed sources were analyzed and compared to identify similarities and differences. A critical assessment of the quality of evidence in each source also considered the limitations mentioned in the reviewed studies, as well as those recognized by the author, considering the applied methodology and sample size. The final findings were synthesized to provide answers to the research questions concerning the impact of AI on contemporary business.
The main topics addressed in the articles include the application of AI in modern business and its effects on processes, performance, and innovation, with particular attention to reliability, transparency, and data availability. We also examined how AI transforms business models, optimizes decision-making, and enhances business efficiency. In addition, the article contains the authors’ predictions about the future application of AI in this context.
Relevant evidence and data on the impact of AI on contemporary business were grouped into several categories, including the use of AI in different industries, its influence on strategic decision-making, and its role in creating competitive advantages for companies.
As illustrated in the flow diagram for literature selection (Figure 1), the search initially identified 122 studies and articles. By applying the established selection process through five levels—title, keywords, abstract, relevance of the topic, and conclusions—the number of relevant studies was narrowed down to 23, which were analyzed in detail and synthesized in this review.
Special attention was given to literature that provided insights into the direct or indirect impact of AI on business processes, value creation, and ethical principles of AI application. The reputation of the authors was assessed based on citation counts, while the reputation of scientific articles was evaluated using impact factors obtained from the academic databases included in the search. Selected sources had to meet criteria of reliability and validity, considering the applied methodology, sample size, instrument validity, and other factors influencing the quality of data.
The authors carefully assessed the credibility and reliability of the selected sources to ensure that the review’s objectives were achieved. The methodological approach to this critical evaluation included a systematic review of relevant studies and articles in the fields of information and digital technologies, artificial intelligence, economics, and business. To assess methodological quality and identify potential limitations, the CRAAP test (University of the West of Scotland, 2022) was used. Applying the CRAAP criteria (Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy, and Purpose) ensured the relevance and reliability of the information and findings from the selected sources. This provided adequate information and a high level of reliability in addressing the objectives and purpose of the review. Nevertheless, it should be noted that certain limitations exist in the selected sources, which were transparently acknowledged with the aim of creating a comprehensive overview of the results obtained.
Review of Primary Sources of Evidence
The results of the individual sources of evidence were synthesized in the table provided in Appendix 1 of this article. Based on the analysis of the available literature that met the relevance criteria, it can be concluded that AI has become a significant factor in contemporary business. Organizations that aim to ensure further development and growth must inevitably focus on the implementation of AI solutions into their business processes. On the other hand, the use of AI in company operations generates an increase in productivity, which creates conditions for sustainable economic development and enables the formation of competitive advantages (Maslak et al., 2021).
The analysis also indicates that the field of AI application in business is still in its early stages. Although there is notable interest from both the academic community and business practice, there is a clear need for further research and deeper segmentation of studies across different business domains and processes.
The impact of AI on contemporary business is undeniably significant. Its advantages, such as the rapid and precise processing of large volumes of data, process automation, and improvements in efficiency, make it an indispensable resource for many companies.
Table 1. Synthesis of Research Results
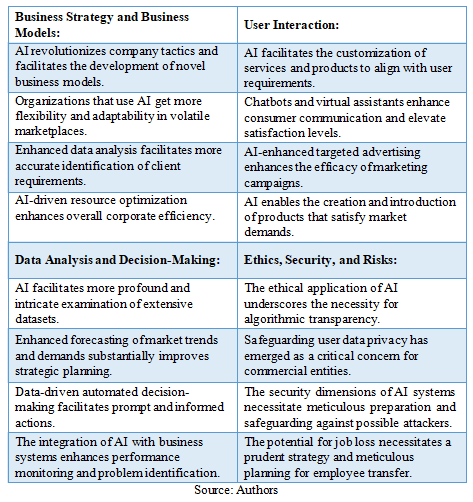
Organizations that successfully implement AI into their operations have the opportunity to generate substantial innovations through new business models and processes, thereby creating the potential to transform the global competitive landscape (Lee, Suh, Roy, & Baucus, 2019).
However, this progress also raises numerous questions and concerns. One of the main issues relates to data privacy and security. AI requires access to large datasets, which may lead to potential misuse or data breaches. Moreover, as with all new technologies, the application of AI in business has certain limitations, including insufficient awareness among decision-makers about the potential benefits of implementation, low levels of IT competencies, underdeveloped IT infrastructure, and the need to design customized solutions for each business organization (Grünbichler, 2023; Žikić et al. 2022).
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence, as one of the modern digital technologies, is becoming an important factor in the development of business organizations and has a strong influence on contemporary business. The impact of AI can be considered from several aspects: business efficiency and business strategy, interaction with users, support to business analytics and decision-making, as well as ethical and social issues. The use of AI in business brings clear advantages, such as faster data processing, automation of processes, and better efficiency, but at the same time it creates risks. Because of that, each company has the challenge to find its own way to implement AI and to manage the risks that come with it.
This review shows that AI is not only a new trend but also a strategic resource for companies that want to stay competitive in the long term. Further development of information and communication technologies, the regulatory environment, and the fast changes on the global market suggest that AI will in the future become one of the tools without which companies cannot operate. According to Gonzalez-Tejero et al. (2023), the cooperation between academia, business organizations, and regulators should be used to develop principles that will help sustainable use of AI technologies and their introduction into business practice.
This article also points out several limitations. One limitation is the lack of access to some articles and the relatively narrow literature search, which means that some relevant works may have been left out. Another limitation is that only literature about company operations was used, while technical and technological aspects of AI were not included. In addition, the choice of sources could have been affected by the authors’ bias. This means that some relevant articles might have been excluded from the final review because of subjective judgment during the selection process.
Since this is a relatively new topic and technology is changing very fast, many authors agree that current research does not cover all aspects of the problem. Some studies are based on a small number of sources, while others rely on assumptions that can easily change over time. Because AI develops quickly, research in this field also needs to be updated often and followed continuously.
AI is both an opportunity and a challenge. It can have an impact on developing new business models, better efficiency, and innovation, but at the same time, the potential risk that this technology carries requires responsible use, ethical standards, and careful regulation.
Reference
2.Ao, J. (2025, June). Research on the impact of artificial intelligence on corporate sustainability performance and its mechanisms: an empirical analysis based on text analysis. Discover Artificial Intelligence, 5(122), 1-16.
3.Bharadiya, J. (2023, June). The impact of artificial intelligence on business processes. European journal of technology, 7, 15–25. doi:10.47672/ejt.1488
4.Bickley, S. J., Chan, H. F., & Torgler, B. (2022, March). Artificial intelligence in the field of economics. Scientometrics, 127, 2055–2084. doi:10.1007/s11192-022-04294-w
5.Bučalina Matić, A., Trifunović, D., & Blanuša, A. (2024). Značaj adekvatnog upravljanja otpadom i reciklaže u zaštiti životne sredine. Društveni horizonti, 4(7), 71-90. https://doi.org/10.5937/drushor2407071B
6.Butenko, E. (2018, January). Artificial intelligence in banks today: Experience and perspectives. Финансы и кредит, 24, 143–153. doi:10.24891/fc.24.1.143
7.Canhoto, A. I., & Clear, F. (2020, March). Artificial intelligence and machine learning as business tools: A framework for diagnosing value destruction potential. Business Horizons, 63, 183–193. doi:10.1016/j.bushor.2019.11.003
8.Čavlin, M., Vapa Tankosić, J., Davidovac, Z., & Ivaniš, M. (2023). Analiza faktora rizika finansijske i profitne pozicije u cilju unapređenja vitalnosti sektora energetike. Oditor, 9(2), 22-
53. https://doi.org/10.5937/Oditor2302022C
9.Dash, R., McMurtrey, M. E., Rebman, C. M., & Kar, U. K. (2019, July). Application of artificial intelligence in automation of supply chain management. Journal of strategic innovation and sustainability, 14, 43–53. doi:10.33423/jsis.v14i3.2105
10.Dašić, B., Pavlović, N., & Savić, M. (2024). Technological Progress and Digitalization in the Function of the Development of E-Education in Serbia. Akcionarstvo, 30(1), 257-279.
11.Davenport, T. H., Guha, A., Grewal, D., & Bressgott, T. (2019, October). How artificial intelligence will change the future of marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48, 24–42. doi:10.1007/s11747-019-00696- 0
12.Di Vaio, A., Palladino, R., Hassan, R., & Escobar, O. (2020, December). Artificial intelligence and business models in the sustainable development goals perspective: A systematic literature review. Journal of Business Research, 121, 283–314. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.08.019
13.Enholm, I. M., Papagiannidis, E., Mikalef, P., & Krogstie, J. (2021, August). Artificial Intelligence and Business Value: a Literature Review. Information Systems Frontiers, 24, 1709–1734. doi:10.1007/s10796-021-10186-w
14.Figura, M., Juracka, D., & Imppola, J. (2025). Management Dynamics in the Knowledge Economy, 13(2), 120-147.
15.Funk, P. (2022). Artificial intelligence and cybersecurity implications for business management. Journal of International Scientific Publications, 16, 252–261. doi:10.6084/m9.figshare.21550926.v1
16.González-Tejero, C. B., Ribeiro-Navarrete, B., Cano-Marin, E., & McDowell, W. C. (2023, February). A Systematic Literature Review on the role of Artificial intelligence in entrepreneurial activity. International Journal on Semantic Web and Information Systems, 19, 1–16. doi:10.4018/ijswis.318448
17.Grünbichler, R. (2023, June). Implementation barriers of artificial intelligence in companies. Proceedings of FEB Zagreb ... International Odyssey Conference on Economics and Business, 5, 193–203. doi:10.22598/odyssey/2023.5
18.Hentzen, J. K., Hoffmann, A. O., Dolan, R., & Pala, E. (2021, November). Artificial intelligence in customer-facing financial services: a systematic literature review and agenda for future research. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 40, 1299–1336. doi:10.1108/ijbm-09-2021-0417
19.Huang, M.-H., & Rust, R. T. (2018). Artificial intelligence in service. Journal of Service Research, 21(2), 155-172.
20.Ilić, V., Mihajlović, M., & Knežević, M. (2022). Uloga socijalnog preduzetništva u savremenim uslovima poslovanja. Oditor, 8(2), 75-
90. https://doi.org/10.5937/Oditor2202074I
21.Janković, G., & Golubović, M. (2025). Cirkularna ekonomija kao osnova održivog razvoja danasnjice. Održivi razvoj, 7(1), 31-62.
22.Jobin, A., & Ienca, M. (2019, September). The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nature Machine Intelligence, 1, 389–399. doi:10.1038/s42256- 019-0088-2
23.Jorzik, P., Klein, S., Kanbach, D., & Kraus, S. (2024, September). AI-driven business model innovation: A systematic review and research agenda. Journal of Business Research, 182(18). doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2024.114764
24.Kitsios, F., & Kamariotou, M. (2021, February). Artificial Intelligence and Business Strategy towards Digital Transformation: A Research Agenda. Sustainability, 13, 2025. doi:10.3390/su13042025
25.Krunić, N., Stojmenović, G., & Kukolj, S. (2023). Uloga i značaj revizijskog uzorkovanja u savremenom preduzeću. Oditor, 9(1), 1-
16. https://doi.org/10.5937/Oditor2301001K
26.Kumar, S., Lim, W. M., Sivarajah, U., & Kaur, J. (2022, April). Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain Integration in Business: Trends from a Bibliometric-Content Analysis. Information Systems Frontiers. doi:10.1007/s10796-022-10279-0
27.Lee, J., Suh, T., Roy, D., & Baucus, M. (2019). Emerging Technology and Business Model Innovation: The Case of Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 5(3), 44.
28.Loureiro, S. M., Guerreiro, J., & Tussyadiah, I. (2021, May). Artificial intelligence in business: State of the art and future research agenda. Journal of Business Research, 129, 911–926. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.11.001
29.Machucho, R., & Ortiz, D. (2025, April). The Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Business Innovation: A Comprehensive Review of Applications, Organizational Challenges, and Ethical Considerations. Systems, 13(4), 1-34.
30.Majstorović, A. & Obrić B. (2023). Principi za poboljšanje dosadašnjeg stanja interne budžetske revizije. Finansijski savetnik, 28(1), 51-68
31.Maslak, O., Maslak, M., Grishko, N., Hlazunova, O., Pererva, P., & Yakovenko, Y. (2021). Artificial Intelligence as a Key Driver of Business Operations Transformation in the Conditions of the Digital Economy. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Modern Electrical and Energy Systems (MEES). doi:10.1109/mees52427.2021.9598744
32.Mihajlović, M., & Todorov, J. (2024). Analiza uticaja nedostatka resursa i satisfakcija stanovništva. Održivi razvoj, 6(1), 47-
62. https://doi.org/10.5937/OdrRaz2401047M
33.Mihajlović, M., Savić, A., Šarčević, V. (2025). Stages in the consumer
buying decison-making process. Mest Journal, 13 (2), 166-176. https://doi.org/10.12709/mest.13.13.02.14
34.Perifanis, N.-A., & Kitsios, F. (2023, February). Investigating the Influence of Artificial intelligence on business Value in the Digital Era of Strategy: A Literature Review. Information, 14(2), 85. doi:10.3390/info14020085
35.Praća, N., Krstić, S., & Božić, N. (2024). Vrste i metode povećavanja viška
vrednosti. Održivi razvoj, 6(2), 35-47.
36.PWC. (2020). Sizing the prize - What’s the real value of AI for your business and how can you capitalise? Retrieved 20.07.2025 from: https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/issues/analytics/assets/pwc-ai-analysis-sizing- the-prize-report.pdf
37.Russell, S. J., & Norvig, P. (2016). Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (3rd ed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
38.Savić, A., Mihajlović, M. & Kostić, R. (2025a). Reconciliation of amounts in budget execution reports and financial statements using the example of the food and agriculture organization of the United Nations. Economics of agriculture, 72 (4), 1163-1183. https://doi.org/10.59267/ekoPolj25041163S
39.Savić, A., Kostić, R. & Ivanova, B. (2025b). Uloga finansijskog izveštavanja u poreskoj evaziji. Megatrend revija, 22(1), 75-100. https://doi.org/10.5937/MegRev2501075S
40.Sira, M. (2022, January). Artificial Intelligence and its Application in Business Management. Zeszyty Naukowe, 2022, 307–346. doi:10.29119/1641-3466.2022.165.23
41.Stanković, T., Čerović, S., & Panić, A. (2023). Role and Application of Information Communication Technologies: Significance of Social Networks in Placement of Hotel Capacities in Serbia. Akcionarstvo, 29(1), 63-94.
42.Svetlana, N., Norkina, A., Makar, S., Tatiana, G., & Medvedeva, O. E. (2022, January). Artificial intelligence as a driver of business process transformation. Procedia Computer Science, 213, 276–284. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2022.11.067
43.Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O'Brien, K. K., Colquhoun, H., Levac, D.,
. . . Straus, S. E. (2018, October). PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-SCR): Checklist and explanation. Annals of Internal Medicine, 169, 467–473. doi:10.7326/m18-0850
44.University of the West of Scotland. (2022). Evaluating Sources: CRAAP Test. Retrieved 29.05.2025 from: https://uws- uk.libguides.com/evaluating_sources/craap_test
45.Vladisavljević, V., Mičić, S & Zupur, M. (2023). Analiza kao osnov za
donošenje poslovnih odluka. Finansijski savetnik, 28(1), 7-35
46.Von Krogh, G. (2018, December). Artificial Intelligence in Organizations: New Opportunities for Phenomenon-Based Theorizing. Academy of Management discoveries, 4, 404–409. doi:10.5465/amd.2018.0084
47.Weber, M., Engert, M., Schaffer, N., Weking, J., & Krcmar, H. (2022, June). Organizational Capabilities for AI Implementation—Coping with Inscrutability and Data Dependency in AI. Information Systems Frontiers. doi:10.1007/s10796-022-10297-y
48.Žikić, S., Trifunović, D., Lalić, G., & Jovanović, M. (2022). Awareness of the population in rural regions of Serbia about renewable energy sources. Ekonomika poljoprivrede, 69(1), 43-56. https://doi.org/10.5937/ekoPolj2201043Z
Objavljeno u
God. 11 Br. 3 (2025)
Ključne reči
🛡️ Licenca i prava korišćenja
Ovaj rad je objavljen pod Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
Autori zadržavaju autorska prava nad svojim radom.
Dozvoljena je upotreba, distribucija i adaptacija rada, uključujući i u komercijalne svrhe, uz obavezno navođenje originalnog autora i izvora.
Zainteresovani za slična istraživanja?
Pregledaj sve članke i časopise
